Sequencing
- Sequencing
- Peptide sequence via MSn
- Cyclic peptides
For peptide sequencing we use the MS/MS method. Whether complete elucidation of the sequence is possible or not depends on the nature of the sequence. For peptides containing 20-30 amino acid residues, complete sequence elucidation is usually possible.
Difference between Edman and MSn sequencing:
Whereas Edman degradation starts at the N-terminus and proceeds sequentially to the C-terminus, MSn fragments the complete molecule. As a consequence:
Under certain circumstances Edman can fail after a couple of amino acids whereas
MS/MS can fail for longer peptides primarily at the N- and/or C-terminus.
In contrast to Edman degradation, MS/MS can fail only for a short part of the sequence but verifying the sequence on both sides of the unverified part.
- For information about limitations of the methods download PDF.
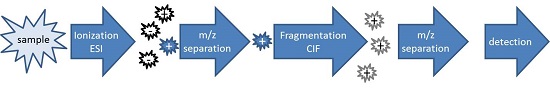
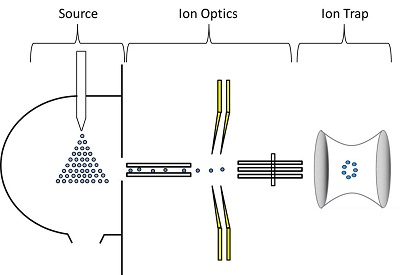
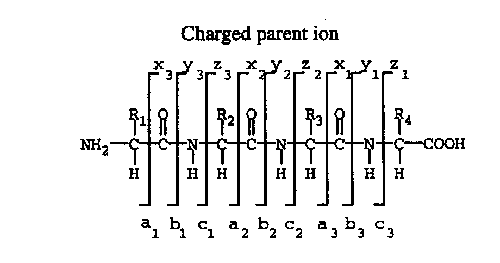
MSn or the combination HPLC-MSn can be offered for peptide sequencing, for the determination of the molecular mass of peptides and for the identification of side products. If necessary, separation can be performed using HPLC on suitable columns. Peaks are detected by diode array detector and transferred online into the mass spectrometer. After electro-spray ionization (ESI) the components are identified by MSn.
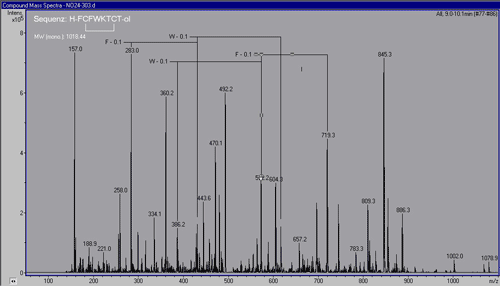
Results: Molecular mass y,
b and a-type fragments found.
The determined peptide sequence.
- For a description of the method please contact info@cat-online.com
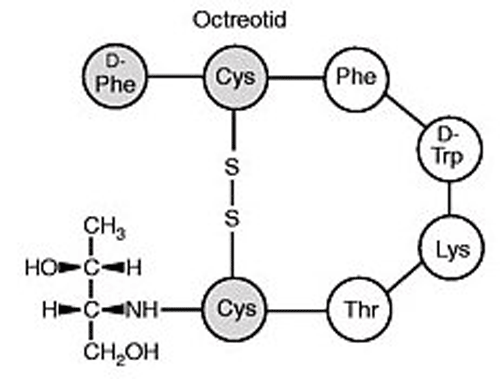
Prior to sequencing of cyclic peptides with a disulfide bridge, the ring structure must be opened selectively.
After disulfide cleavage with DTT
(1,4-Dithio-DL-threitol), the molecular weight is checked to be 2 mass units higher than for the cyclic peptide and the linear peptide is subsequently
sequenced.